
Basic knowledge of pneumatic valve control accessories
1. Air source pipe:
A gas source pipe is a piping system that provides a stable gas supply for pneumatic instruments to ensure their normal operation.
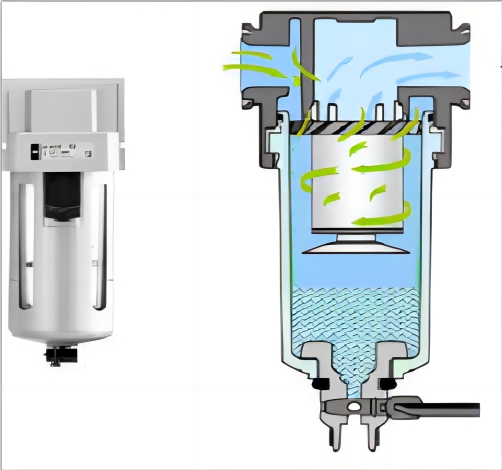
2. Filter pressure reducing valve
Filter pressure reducing valve is a common pneumatic control component, whose main function is to filter and reduce the pressure of the gas entering the valve body, ensuring the stability and cleanliness of the gas, and meeting the needs of industrial production and laboratory applications.
When the pressure at the input end fluctuates, the filter pressure reducing valve will automatically make corresponding adjustments to ensure stable pressure output and achieve the goal of ensuring pressure stability. Specifically, the filtering and pressure reducing valve
The working principle is as follows:
Air inlet: The air inlet of a filter pressure reducing valve is usually a pipe or hole used to introduce high-pressure gas into the valve body.
Filter: The gas entering the valve body first passes through the filter, and through this process, the outlet of the valve is prevented from entering impurities and dust. A filter is usually composed of one or more filter screens, used to filter out impurities and particles in the gas and ensure the cleanliness of the gas.
Pressure reducer: The gas filtered by the filter passes through the pressure reducer, and the gas pressure is reduced to the required working pressure. Pressure reducers usually use springs or diaphragms as control components, connected to the air inlet. When the gas pressure reaches the set value, it will automatically open or close, thereby controlling the size of the gas pressure.
Gas outlet: After passing through filters and pressure reducers, the gas is discharged through the outlet pipeline and supplied to the required equipment or workplace for use.
In the above process, filtration and pressure reduction are two independent but closely related steps, which are the key to ensuring the normal operation of the filtration pressure reducing valve.
3. Pneumatic amplifier:
Pneumatic amplifier is a device that amplifies the input pneumatic signal by utilizing the pressure difference generated by gas flow. Its working principle is mainly based on the closed chamber principle, which introduces compressed air into a closed room, and then changes the volume of the room by controlling the opening and closing of the valve, thereby amplifying the input pneumatic signal.
When the input pneumatic signal enters the pneumatic amplifier, it will cause the valve inside the amplifier to act, changing the on/off situation of the pneumatic circuit. In this way, compressed air will enter or exit different rooms or chambers of the amplifier according to the size and direction of the input signal, forming different output pneumatic signals.
Specifically, when the input signal increases, the pneumatic amplifier will open the valve to increase the room volume, thereby increasing the output pneumatic signal; When the input signal decreases, the pneumatic amplifier will close the valve, causing the room volume to decrease, thereby reducing the output pneumatic signal. In this way, the weak aerodynamic signal input can be amplified into a strong aerodynamic signal by the amplifier.
In addition, pneumatic amplifiers can also be used to improve the action speed of actuators and reduce the time lag of long-distance transmission of pressure signals. Due to its wide range of applications, pneumatic amplifiers have become one of the important components in pneumatic control systems, instrumentation, and other fields.
4. Holding valve/locking valve:
Pneumatic holding valves and locking valves are important components in pneumatic control systems, used to control gas flow and pressure. This article will provide a detailed introduction to the working principles of pneumatic positioning valves and locking valves, mainly including the following aspects:
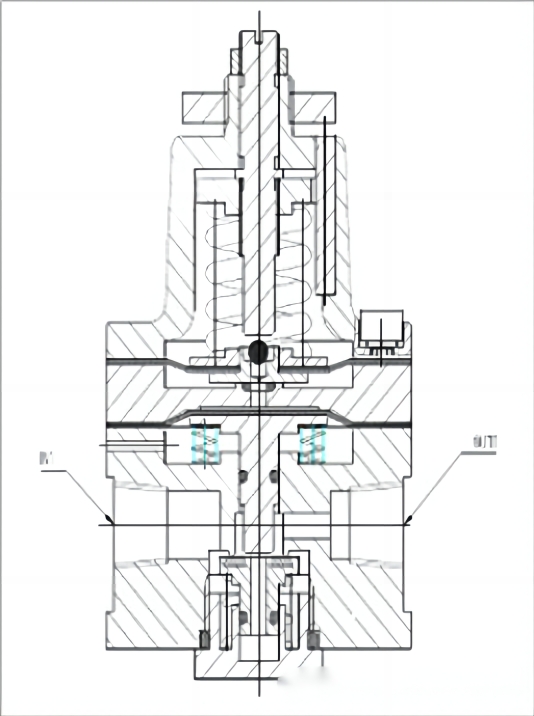
Pressure perception:
Pneumatic holding valves and locking valves are usually equipped with sensors or switches that sense pressure changes. When the pressure of the gas exceeds or falls below the predetermined value, the sensor will send a signal, triggering subsequent actions.
Valve core action:
When the signal from the pressure sensor triggers the action of the valve core, the control valve of the pneumatic holding valve or locking valve will adjust the internal gas flow based on the received signal. This action will change the size of the channel through which gas enters or exits the valve body, thereby regulating the pressure of the system.
Lock/Unlock:
After sensing a signal exceeding the predetermined pressure, the pneumatic positioning valve will lock the valve in a certain position through an internal mechanism to prevent valve misoperation caused by pressure fluctuations. The locking valve will quickly close or open the channel upon sensing the pressure signal, preventing gas backflow.
Maintain pressure:
Whether it is a pneumatic holding valve or a locking valve, one of its main functions is to maintain stable system pressure. When feeling a change in pressure, the valve will adjust its own state to maintain the system pressure within the set range.
Automatic reset:
In some cases, when the pressure source causing valve action disappears, the pneumatic holding valve and locking valve will automatically reset, return to the initial state, and prepare for the next action. The automatic reset function ensures that the valve can quickly restore its normal working state without the need for manual intervention.
5.Pneumatic valve
Gas control valve is a mechanical device commonly used in industrial control, which can regulate and control gas flow rate. The working principle of a gas control valve is to control the flow rate by changing the pressure of the gas.

Categories
Recent Posts
Copyright © 2024 Tonglu Yongxin Valve Co.,Ltd.All Rights Reserved. Powered by dyyseo.com

IPv6 network supported